Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil by using mineral nutrient solutions in water. It’s also referred to as “soilless gardening.” This agricultural technique has been gaining popularity as a sustainable way to achieve higher crop yields without the need for soil. But does hydroponics really not need any soil to thrive?
What Are The Basics of Hydroponic Systems?
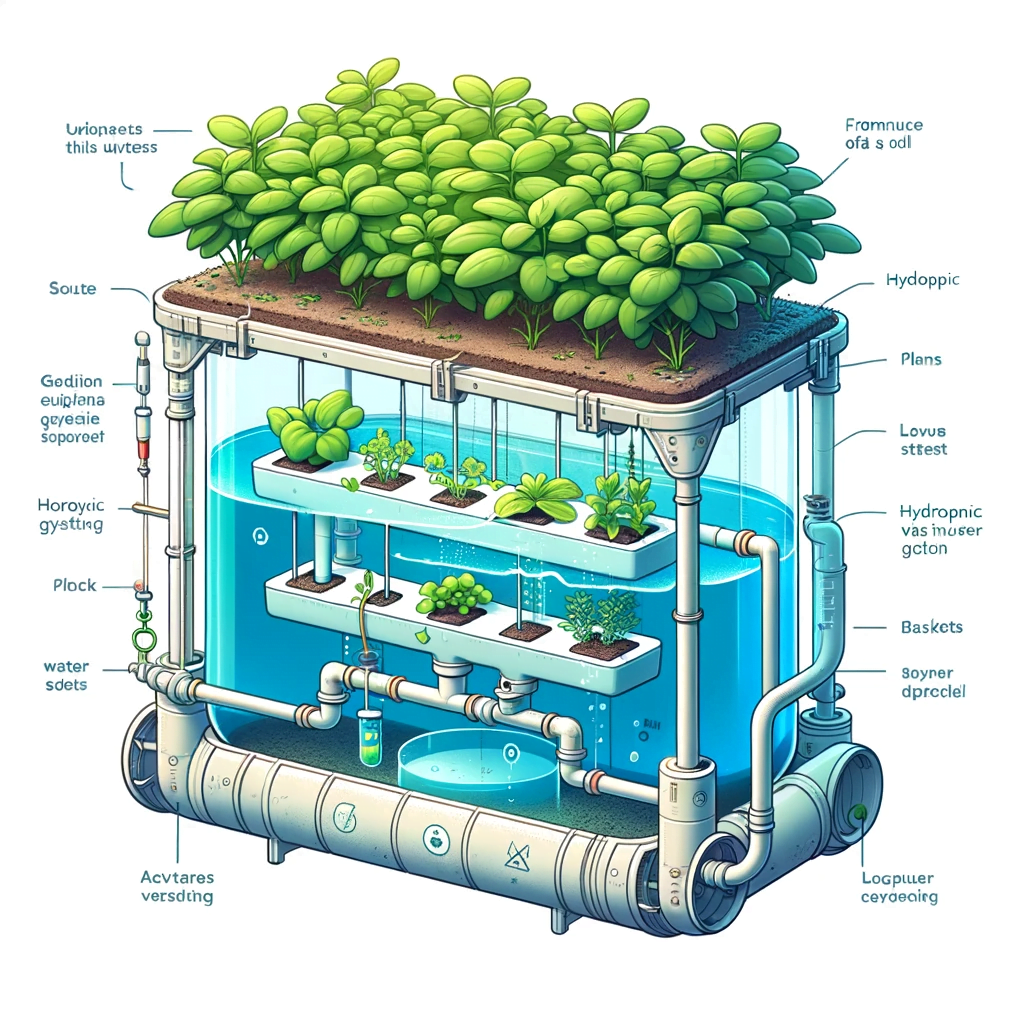
Hydroponics requires only three essential components:
- The nutrient solution that provides minerals for growth
- A medium for the roots to grow in like perlite, clay pellets, coconut coir, etc.
- Lighting for photosynthesis
There are several main types of hydroponic systems that supply nutrients and water:
- Wick systems use absorbent wicks to take up nutrient solution to plant roots
- Water culture continuously suspends roots directly in an oxygenated nutrient bath
- Ebb and flow periodically floods the roots then drains away the solution
- Drip systems use a timer to deliver nutrient solution to each plant as needed
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) creates a constant shallow stream of nutrients along sloped channels
- Aeroponic systems mist roots suspended in air with a nutrient solution
- Deep Water Culture where roots dangle in an aerated, nutrient-rich reservoir
- Wick systems bring nutrients to roots through capillary action via wicks
- Hybrid systems combine multiple techniques like NFT and water culture
The choice of hydroponic system depends on factors like crop type, environment, scale, and budget. Systems can be designed for everything from small indoor grows to massive commercial greenhouses.
While hydroponics doesn’t use soil, plants still require support and stability. Different hydroponic media options include:
- Perlite
- Vermiculite
- Coco coir
- Gravel
- Expanded clay pellets
- Rockwool
- Sand
- Pumice
- Peat moss
The growing medium anchors the plant while allowing the roots to access oxygen and nutrient solution. Media is chosen based on drainage, aeration, and other factors.
What Are The Benefits of Hydroponic Gardening?
Growing plants hydroponically offers many advantages compared to conventional soil gardening:
- Faster growth rate and larger yields since the roots get constant access to nutrients
- No weeding or tilling since there is no soil, reducing labor
- Optimized nutrition by customizing the mineral solution for each plant’s needs
- Lower water usage because there’s no runoff or evaporation from soil
- Ability to grow plants anywhere without relying on natural soil quality
- Less chances of soil-borne diseases by growing in a sterile medium
- Higher density cultivation since space isn’t taken up by soil
- Less environmental impact with recycling and containment of nutrient runoff
With hydroponics, you can gain precise control over the plant’s growing environment and cater conditions to maximize growth and quality.
What Plants Work Best With Hydroponics?
Many vegetables and fruits grow exceptionally well hydroponically, including:
- Tomatoes
- Lettuce
- Peppers
- Cucumbers
- Herbs like basil, parsley, oregano
- Strawberries
- Melons
- Squash
- Beans
- Peas
- Broccoli
Leafy greens and herbs are especially productive with hydroponics, achieving rapid, abundant growth. However, most flowering and fruiting plants can be grown hydroponically with success. Even ornamental flowers and some trees can use soilless systems.
Factors like lighting, temperature, nutrients, and growing medium can all be optimized in controlled indoor systems to allow many plants to exceed their potential yield and quality.
With hydroponics, growers can surpass the limitations and seasonal variations of local climate. Tropical fruits like mangos can be grown in temperate regions. Cool weather crops like kale can thrive year-round in indoor facilities. The possibilities are vast with complete control over soilless environment.
Creating Your Own Hydroponic System
You can create a productive hydroponic system right at home with basic equipment and supplies. Here’s how to get started:
Supplies Needed
- Growing containers like net pots, baskets, or buckets
- Nutrient solution with essential minerals
- Air pump and tubing for aeration
- Grow lights like LEDs or fluorescent bulbs
- pH testing kit
- Hydroponic nutrients like MaxiGro, FloraNova, General Hydroponics, etc.
- Seed starters like Rockwool cubes
Equipment
- Plastic bin, bucket, or tray for reservoir
- Growing medium like perlite, clay pellets, coconut coir
- Air stones, diffusers, or bubblers for oxygenation
- Water pump and irrigation system if needed
- Net trellis, poles, cages for climbing plants
- Propagation domes or humidity tents
- Humidity and temperature monitors
- Water filtration systems as needed
Step-by-Step Setup
- Fill reservoir bin with pre-mixed nutrient solution.
- Place growing medium in containers like net pots.
- Transplant seedlings or cuttings into the medium.
- Suspend containers over reservoir to access nutrients.
- Set up pump and tubing to oxygenate solution.
- Position grow lights above plants.
- Test and adjust pH, nutrients routinely.
- Train and trellis plants as needed.
DIY systems can be made from plastic bins, PVC pipes, and other household items. More advanced systems include automation of lighting, irrigation, and monitoring.
Grow lights, nutrients, and other hydroponic equipment are easily available online or at garden stores. Basic systems can be created for less than $300. More robust permanent systems with higher yields cost $600-$1000 or more.
Troubleshooting Common Hydroponic Issues
While soilless systems offer increased control, they can run into problems. Here are some common issues and how to resolve them:
- Nutrient deficiencies – Test levels and adjust mineral solution accordingly
- Equipment malfunctions – Check pumps, aeration, timers, lighting and fix issues
- Algae growth – Block light to reservoir, use opaque tubing, add H2O2
- Root rot – Increase oxygenation and reduce temperature of solution
- Slow growth – Upgrade lighting, change nutrients, test pH
- Tip burn – Lower nutrient strength if excessive salts build up
- Poor flowering/fruiting – Increase phosphorus levels in nutrient mix
Careful monitoring and maintenance helps prevent disruptions in optimal conditions.
Hydroponics vs Soil Gardening
While hydroponics offers many advantages, traditional in-ground soil gardening still retains some benefits:
- Lower startup costs – Dirt is cheaper than hydroponic setups
- Natural buffering – Soil balances and stabilizes pH fluctuations
- Established techniques – Thousands of years of gardening knowledge and practices
- Organic approaches – Avoidance of synthetic nutrient formulas
- Native soil ecology – Complex networks of microbes and fungi
However, advancements in hydroponics are bridging gaps with soil gardening. Lower cost options, buffered nutrient solutions, and organic hydroponics gain some of the same benefits.
In the end, hydroponics complements soil gardening with higher productivity, space efficiency, and environmental control. Blending both methods allows each to play to their strengths.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hydroponics
Do hydroponic plants really grow faster?
Yes, most plants grow at a faster rate with hydroponics vs soil. With constant access to nutrients and optimized conditions, plants spend less time developing roots and more energy on vegetative growth above ground.
Is hydroponics more expensive than soil gardening?
The startup costs can be more, but over time hydroponics can become more productive and cost-efficient. Savings result from reduced water usage, space efficiency, and labor compared to soil methods.
What vegetables grow best hydroponically?
Leafy greens like lettuce, herbs, tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and fruiting plants tend to thrive with hydroponics and produce abundant yields.
Can hydroponics be organic?
Yes, organic hydroponic systems use inputs like fish emulsion, compost teas, worm castings, and avoid synthetic fertilizers. However, hydroponics is not allowed under USDA organic certification.
Are hydroponic plants as nutritious?
Plants grown hydroponically can be just as nutritious or even more nutrient-rich. With optimized conditions, plants are less stressed and able to focus energy on growth rather than survival.
The Future of Hydroponics
Advancements in hydroponics are expanding this cultivation method from small hobby greenhouses to large commercial facilities producing tons of produce.
Other emerging uses include:
- Rooftop urban farms
- Produce grown in retail stores and restaurants
- Edible land



